Health
Explore Health
-
Ageing
-
Ageing
-
Alcohol
-
Alcohol
-
Allergies
-
Allergies
-
Anatomy
-
Anatomy
-
Autism
-
Autism
-
Death
-
Death
-
Diabetes
-
Diabetes
-
Exercise
-
Exercise
-
Fertility, Pregnancy & Birth
-
Fertility, Pregnancy & Birth
-
Food & Diet
-
Food & Diet
-
Genetics
-
Genetics
-
Heart & Circulation
-
Heart & Circulation
-
Immune System
-
Immune System
-
Medicine & Drugs
-
Medicine & Drugs
-
Mind
-
Mind
-
Obesity
-
Obesity
-
Sex
-
Sex
-
Sleep
-
Sleep
-
Smoking
-
Smoking
-
Supplements & Vitamins
-
Supplements & Vitamins
-
Surgery
-
Surgery
-
Viruses, Infections & Disease
-
Viruses, Infections & Disease
Editor's Picks
Latest about Health

How does CRISPR work?
By Kamal Nahas last updated
CRISPR is a versatile tool for editing genomes and has recently been approved as a gene therapy treatment for certain blood disorders.
Why genetic testing can't always reveal the sex of a baby
By Maggie Ruderman, Kimberly Zayhowski published
Gender and sex are more complicated than X and Y chromosomes.

What causes you to get a 'stitch in your side'?
By Clarissa Brincat published
Many people are familiar with the sharp pain that can strike beneath your rib cage during exercise. But what causes it?

'We're proving that this is a new door to understand cancer better': Tour de France coach Iñigo San Millán on what elite cyclists could reveal about cancer biology
By James Witts published
Cancer researcher Iñigo San Millán is also a coach to Tadej Pogačar, a favorite to win this year's Tour de France. In this interview, San Millán discusses his work in both arenas.
Single molecule reverses signs of aging in muscles and brains, mouse study reveals
By Nicoletta Lanese published
A new study in mice and human cells suggests that a small molecule can help reverse signs of aging by extending telomeres and modulating key genes.
Body parts grown in the lab
By Mindy Weisberger, Emily Cooke last updated
In recent years, scientists have successfully grown a range of miniature organs and human body parts in the lab.
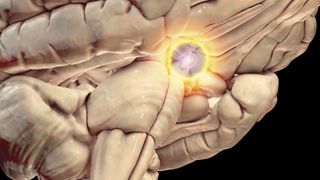
Predator or prey? This 'switch' in the brain toggles when you're hunting or being hunted
By Stephanie Pappas published
The hypothalamus, a brain region that helps control our hormones and sleep cycles, is also responsible for our ability to switch between predator- and prey-like behavior.

H5N1 bird flu can remain infectious in raw milk for at least an hour, study finds
By Kristel Tjandra published
Scientists found that contaminated milking equipment can harbor the H5N1 virus for more than an hour, increasing the risk of dairy farmers getting infected.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.